Structure of an aeroplane(4)
Peaceful Heaven :: Free up zone. :: Hobbies :: 飛機跑道-Here
Page 1 of 1
 Structure of an aeroplane(4)
Structure of an aeroplane(4)
| LATITUDE & LONGITUDE Page 1-45 |
 |
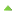
| In the Earth's reference system, the lines that run: east and west are called parallels of latitude because they are parallel with the equator. Each of these parallel lines forms a circle on the face of the earth. Each one is a constant distance north or south of the equator. the equator is latitude 0 degrees and the poles are located at 90 degrees latitude. |
| Lines running north and south, passing through the North and South poles, are called meridians of longitude. Meridians run perpendicular to the equator. The starting point, or 0 degree meridian, is the one passing through Greenwich, England. It is called the prime meridian. the prime meridian serves as the starting point of east-west measurement. |
| 24 HOUR CLOCK Page 1-47 |
 |
| Aviators uses the 24 hour clock. This method prevents confusion between AM and PM. Each minute of the day is represented as a four digit number. The first two digits are the number of hours past midnight, and the second two digits are the number of minutes. Each digit is pronounced separately with "hours" at the end. The day starts at midnight (0000, "zero zero zero zero hours" |
Here are some examples times during the day:
|
| AERONAUTICAL CHARTS Page 1-49 |
 Sectional Chart |
| The most commonly used aeronautical chart is called the sectional aeronautical chart. Sectionals, as they are known, are conic projections and each one represents a small portion of Earth's surface. Some of the data on a chart is superimposed.
|
| COMPASS Ref. pages. 1-52 & 53 |
| The four cardinal points of the compass are north, east, south, and west. These are also known on the 360 degree compass as: 360 degrees (north), 90 degrees (east), 180 degrees (south), and 270 degrees (west). Halfway between each of these cardinal points are the four intercardinal points: northeast, southeast,northwest, and southwest. |
 Locations of the North Pole (true north, TN) and the Magnetic North Pole (MN) |
| All compass needles point towards a large mass of magnetic rock which is in the earth not far from the North Pole. This point is called magnetic north. The compass error that is caused by the magnetic north pole and the geographic North Pole being located at different places is called magnetic variation. |
| PILOTAGE NAVIGATION Page 1-54 |
| Pilotage navigation means navigating by reference to visible landmarks. This can be as basic as
Checkpoint - the place over which the airplane should be at a certain predetermined time. |
| DEAD RECKONING Page 1-56 |
| Dead reckoning navigation is to know by preflight planning and inflight checking, the position of the aircraft at any given time. This is accomplished by calculation, the measuring and keeping account of such navigational factors as heading, distance, time, aircraft speed, and wind direction and velocity. |
Factors used in Dead Reckoning (DR) are:
|
| VECTORS Page 1-57 |
| A vector is a line which has both direction and magnitude. |
| VOR RADIO NAVIGATION Page 1-60 |
| VOR (Very-high-frequency Omnidirectional Radio) is the most extensively used radio navigation system used for aircraft navigation. By the way, Omnidirectional is a fancy word for all directions. A VOR station transmits radio beams called radials which extend out from VOR stations like spokes on a wheel. Each radial is identified by its magnetic direction measured from the station. For example, the radial extending from the station to magnetic South is called the 180 degree radial. Pilots can fly to and from a VOR station simply by following the proper radial. The VOR receiver in the aircraft has the following components:
|

alan200994- Admin
- Number of posts : 607
Age : 29
Location : http://www.xanga.com/alan200994
Registration date : 2008-10-30
Character sheet
Lucky field:


 (1/1)
(1/1) -

 Similar topics
Similar topics» Structure of an aeroplane(5)
» Structure of an aeroplane(1)
» Structure of an aeroplane (2)
» Structure of an aeroplane(3)
» Structure of an aeroplane(1)
» Structure of an aeroplane (2)
» Structure of an aeroplane(3)
Peaceful Heaven :: Free up zone. :: Hobbies :: 飛機跑道-Here
Page 1 of 1
Permissions in this forum:
You cannot reply to topics in this forum|
|
|